Daur Hidrologi dan Peranan Kimia dalam Prosesnya
It’s all part of a fascinating, continuous process called the hydrologic cycle, also known as the water cycle. But this cycle isn’t just about water moving around; it’s deeply intertwined with chemistry! Join us as we explore the intricate relationship between the hydrologic cycle and the chemical reactions that drive it.
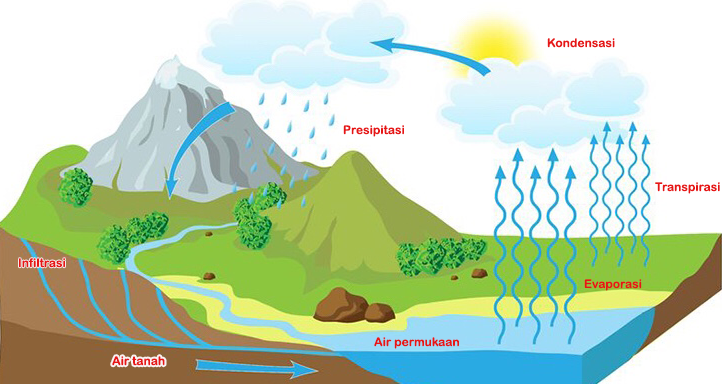
What is the Hydrologic Cycle?
The hydrologic cycle is the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth. It’s a closed system, meaning that the amount of water on Earth remains relatively constant, but it changes form and location constantly. Think of it like a giant, global water park, where water is constantly being recycled and reused!
Key Processes in the Hydrologic Cycle
The hydrologic cycle consists of several key processes, each playing a vital role in the movement and distribution of water:
- Evaporation: The process by which liquid water changes into water vapor (a gas) and rises into the atmosphere. This is primarily driven by solar energy.
- Transpiration: The release of water vapor from plants into the atmosphere through tiny pores called stomata.
- Sublimation: The direct conversion of ice or snow into water vapor, bypassing the liquid phase.
- Condensation: The process by which water vapor in the atmosphere cools and changes back into liquid water, forming clouds.
- Precipitation: Any form of water that falls from the atmosphere to the Earth’s surface, including rain, snow, sleet, and hail.
- Infiltration: The process by which water soaks into the soil and percolates into the groundwater.
- Runoff: The flow of water over the land surface, eventually making its way into rivers, lakes, and oceans.
The Chemical Symphony of the Hydrologic Cycle
While the hydrologic cycle is primarily a physical process, chemical reactions play a crucial role in many of its stages. These chemical interactions influence water quality, atmospheric composition, and even climate patterns. Let’s delve into some key chemical processes within the hydrologic cycle:
1. Dissolution: Water as a Universal Solvent
Water’s unique ability to dissolve a wide range of substances makes it an essential player in chemical reactions. As water moves through the hydrologic cycle, it picks up various chemicals from the atmosphere, soil, and rocks.
-
Acid Rain Formation: Carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere dissolves in rainwater to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), making rainwater slightly acidic. This natural acidity helps to weather rocks and release essential minerals. However, human activities have increased the concentration of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) in the atmosphere, which can dissolve in rainwater to form sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and nitric acid (HNO3), respectively. This results in acid rain, which can harm ecosystems and damage infrastructure.
-
Mineral Weathering: As water infiltrates the soil and bedrock, it dissolves minerals, releasing ions into the groundwater. This process, known as chemical weathering, plays a vital role in shaping landscapes and providing nutrients to plants.
2. Redox Reactions: The Exchange of Electrons
Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, involve the transfer of electrons between chemical species. These reactions are crucial in controlling the fate of many pollutants and nutrients in aquatic environments.





