Perbedaan Campuran dan Senyawa dalam Kimia
Compounds – What’s the Real Difference?
Ever stared into a glass of orange juice, or perhaps marveled at the complexity of a chocolate chip cookie? Have you ever wondered what lies beneath the surface of these everyday marvels, at the chemical level? The answer, in many cases, boils down to understanding the fundamental difference between mixtures and compounds. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of chemistry, exploring the nuances that separate these two important concepts. Get ready to put on your lab coats (metaphorically, of course!) and join us on this exciting journey.
What Exactly Are Mixtures and Compounds? A Foundation
Before we start dissecting the differences, let’s establish a solid understanding of what mixtures and compounds actually are. Think of them as two different ways elements and molecules can come together.
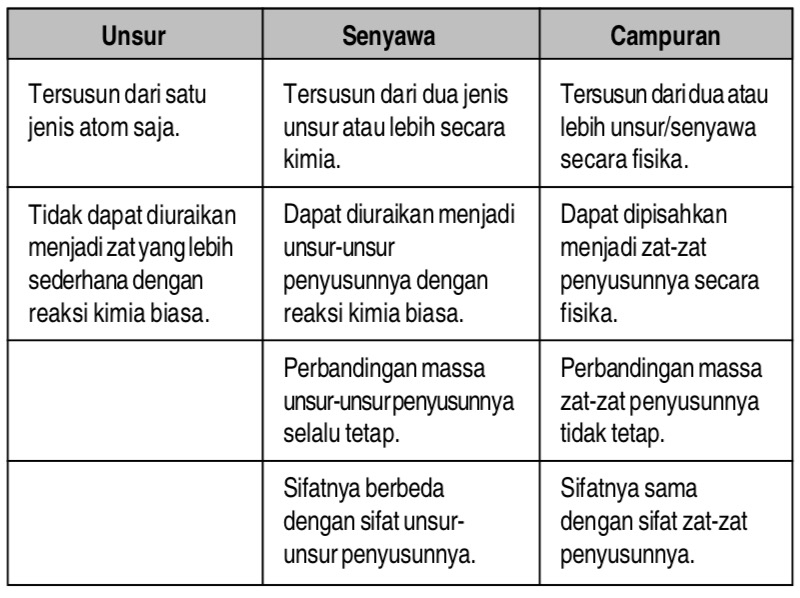
Mixtures: A Casual Gathering of Ingredients
Imagine a salad. You’ve got lettuce, tomatoes, cucumbers, maybe some croutons – all tossed together. Each ingredient retains its individual identity. That’s essentially what a mixture is:
- Definition: A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are physically combined, meaning they are not chemically bonded. Each substance retains its individual chemical properties.
- Key Characteristics:
- Components can be separated by physical means (filtration, evaporation, etc.).
- The composition is variable; you can add more or less of any ingredient.
- The substances retain their individual properties.
Compounds: A Chemical Marriage
Now, imagine baking a cake. You mix flour, sugar, eggs, and butter. But something magical happens in the oven. These ingredients undergo chemical reactions, transforming into something entirely new – a cake! This is analogous to a compound.
- Definition: A compound is a substance formed when two or more elements are chemically bonded together in a fixed ratio.
- Key Characteristics:
- Elements are combined in a fixed, definite proportion.
- Components are chemically bonded and cannot be separated by physical means.
- The compound has properties that are different from the properties of its constituent elements.
The Core Differences: Unveiling the Distinctions
Now that we have a basic understanding, let’s explore the core differences between mixtures and compounds in more detail.
H2: Composition: Fixed vs. Variable
This is a crucial distinction. Think back to our salad and cake analogies.





